MDtool#
MDtool is a console application for configuring and performing basic diagnostics on MD drives via CANdle. It is designed as a complementary tool for APIs, reducing the overhead when setting up the drives for the first time or reconfiguring them. It uses the CANdle C++ library on its backend.
Installation#
The easiest way to install the MDtool is to select the appropriate *.deb package from the MDtool GitHub repo releases page (compliant with your system’s architecture). To install after the download simply call:
sudo apt install ./mdtool_xx-x_xx.deb
After the install please make sure the current user is added to the dialout group using the command:
sudo adduser <current user> dialout
if it wasn’t, please reboot the PC
sudo reboot
It is also recommended to install the setserial package which allows for higher communication speeds:
sudo apt install setserial
Be sure to call
mdtool bus <SPI/UART/USB>
to configure MDtool for the desired communication bus before first use, if you’re using CANdle HAT and SPI or UART bus.
In case the CANdle device still doesn’t work, make sure a /dev/ttyACM0 device is listed when you call:
ls /dev/ttyACM*
Note
For the command prompt to work after the installation you have to restart the terminal window
Commands#
mdtool bus <bus> <device>#
MDtool is able to work with CANdle and CANdle HAT. This is why before the first use it has to be configured for a particular communication bus. Use the bus command to set it to USB, SPI, or UART, based on which device you own. The default bus setting is USB. You don’t have to repeat this setting unless you want to change the current communication bus. The device parameter is optional and can be used in case of the UART and SPI bus, if the default device (/dev/spidev0.0 in case of SPI or /dev/ttyAMA0 in case of UART) is not suitable for your application.
mdtool ping <baud>#
MDtool is able to discover the drives that are connected to the CAN bus. You can ping the drives at a specific speed (1M/2M/5M/8M) or just use the ‘all’ keyword for pinging all speeds in one go.
Note
CANdle does not support working with drives configured with different CAN speeds on the same CAN bus – please make sure when “mdtool ping all” command is executed, all discovered drives lie in a single speed category.
mdtool config zero <ID>#
This command sets the current motor position to zero - from the moment this command is called all encoder measurements are referenced from the current position.
Note
This setting has to be saved to be preserved after power down! Please see the config save
mdtool config can <current ID> <new ID> <baud> <watchdog period [ms]> <termination>#
This command is used to change MD parameters such as CAN ID, CAN speed, and CAN watchdog.
CAN IDs should be in range <10:2000>
Baud should be one of the available speeds (1M/2M/5M/8M)
Watchdog period should be in range <1:2000> ms, 0 disables the watchdog. For more information on CAN watchdog please refer to section FDCAN Watchdog Timer.
Termination should be either 1 to turn the termination on or 0 to turn the termination off.
Warning
Software-controlled termination is available since version HW V2.0. It is an optional setting - when not typed in the command this setting will default to zero (off).
Note
This setting has to be saved to be preserved after power down! Please see the mdtool config save
mdtool config current <ID> <current>#
This command is used to set the maximum phase current that is allowed to flow through the motor when high torques are commanded. By default, the maximum current is set to a rather low value that will not lead to motor or driver burnout. However, this also limits the motor’s maximum torque capabilities. Using the config current command one can increase the maximum current. For the absolute maximum please refer to maximum ratings section.
Warning
The warranty does not include burnout actions due to too high current settings. For max continuous driver current please refer to the general parameters and safety limits sections.
Note
This setting has to be saved to be preserved after power down! Please see the config save
mdtool config bandwidth <ID> <torque bandwidth in Hz>#
This command can be used to change the torque bandwidth without recalibrating the actuator. For more information on the torque bandwidth please see the section about calibration.
Note
This setting has to be saved to be preserved after power down! Please see the config save
mdtool config save <ID>#
For the config commands to take action after the next power cycle a save command has to be executed. This command saves the current drive’s settings to the non-volatile FLASH memory.
mdtool setup calibration <ID>#
This command runs the basic calibration routine. During calibration, the drive has to be able to rotate freely and the power supply should be able to deliver at least 1A of current. For more detail on the calibration process please refer to the calibration section.
mdtool setup calibration_out <ID>#
This command runs the output encoder calibration routine. During output encoder calibration, the drive has to be able to rotate for at least two full rotations of the output shaft and the power supply should be able to deliver at least 1A of current. For more detail on the calibration process please refer to the output encoder calibration section.
mdtool setup motor <ID> <*.cfg>#
This command is used to write a new motor config. For the config file argument one of the *.cfg files from ~/.config/mtool/mdtool_motors/ directory should be passed. Check out the description below for more information on the respective config fields:

mdtool setup info <ID> [all]#
This command is used to read the motor internal parameters. Use an optional ‘all’ keyword at the end of the command to read full parameter set. An example command output might look like this:
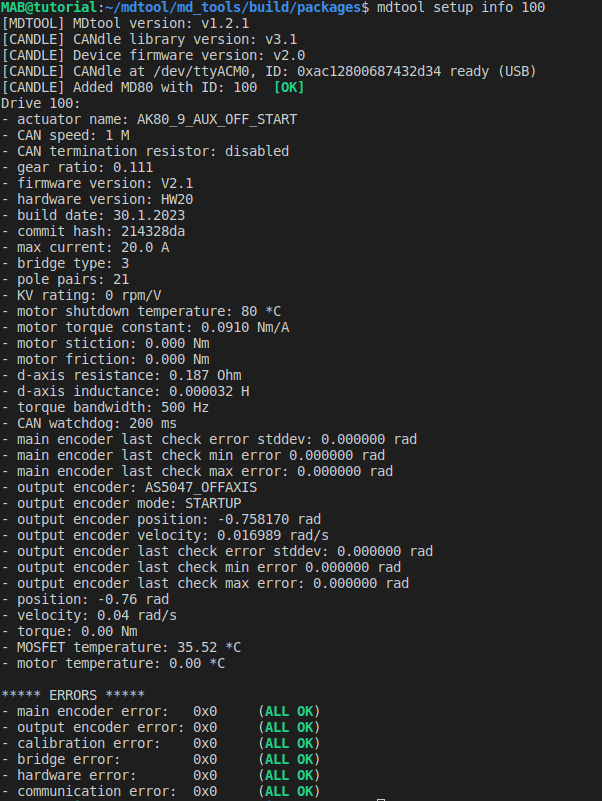
Reading the errors is the easiest way of debugging possible problems with the drive. For errors description please visit the status section.
mdtool blink <ID>#
This command is mostly used to find an MD drive on a long CAN bus using its ID – the command makes the drive flash its onboard LEDs for easy identification.
mdtool test move <ID> <position>#
This command is used to test the actuator movement in impedance mode. It helps to assess if the calibration was successful and if there are no issues visible to the naked eye. The position argument is always the amount of position for the motor to be moved from the current position.
mdtool test move absolute <ID> <target position> <velocity> <acceleration> <deceleration>#
This command is used to test the actuator movement in profile position mode. The motor is going to use acceleration parameter to speed up to velocity parameter and then deceleration parameter to slow down and reach the target position. The move is absolute to the currently set zero position. By providing only the ID and target_velocity the MDxx will use the default acceleration, deceleration and velocity parameters.
mdtool test latency <baudrate>#
This command is used to test the PC<>CANdle communication speed which greatly affects the PC<>MD communication speed. The higher the measured frequency the better.
mdtool test encoder <type> <ID>#
This command is used to check how accurate a praticular encoder was calibrated. The ‘type’ argument can be either ‘main’ for onboard encoder, or ‘output’ for output encoder. This command runs a routine that makes one full rotation of the shaft (either motor or output shaft, depending on the chosen encoder type) and after completing fills up the max, min and standard deviation errors that can be accessed using the mdtool setup info all command.
Warning
Main encoder errors can be larger for non-sinusoidal motors (BLDC motors) because of their back-emf waveform shape. If you care about very precise positioning we advise using PMSM motors (sinusoidal).
mdtool encoder <ID>#
This command is useful when one wants to measure the position of the actuator in the current setup (without writing a custom script). After the command is executed the screen shows the current position of the actuator’s shaft and it does so until you press Ctrl + C.
mdtool clear error <ID>#
This command is used to clear non-critical MDxx errors.
mdtool clear warning <ID>#
This command is used to clear all MDxx warnings.
mdtool register read <ID> <regID>#
This command is used to read a register from MDxx controller.
mdtool register write <ID> <regID> <value>#
This command is used to write a register with value param.
mdtool reset <ID>#
This command is used to reset an MDxx controller.
